About the indicator
Fine particulate matter, or PM2.5, is an air pollutant that can be harmful to human health. PM2.5 consists of very small particles 2.5 micrometres or less in diameter. Exposure to these small particles can cause serious health problems including lung and heart disease.
This indicator reports on the concentration of PM2.5 from 2000 to 2023 and provides information on the variation across Alberta and how concentrations have changed over time. This indicator also compares PM2.5 concentrations with Alberta's Ambient Air Quality Objectives (AAAQOs), which set thresholds for air pollutants to protect human and ecosystem health.
Fine particulate matter facts
- PM2.5 is emitted into the atmosphere from human activities and natural sources such as wildfire smoke. Some PM2.5 is emitted directly into the atmosphere, for example through dust or smoke. PM2.5 also forms through chemical reactions in the atmosphere involving other gases, such as nitrogen dioxide, sulphur dioxide and volatile organic compounds.
- Human caused sources of PM2.5 include burning of fossil fuels for vehicles, home heating, power plants, and industrial processes. Other sources include home wood burning, brush pile burning, road dust, and construction operations, among others.
- In Alberta, the highest concentrations of PM2.5 are typically caused by wildfire smoke and winter smog. Smog is a mixture of gases and particles emitted into the air by human activities. Smog negatively affects human health and forms haze that reduces visibility.
- PM2.5 is part of the Air Quality Health Index (AQHI) that reports on health risks associated with local air quality across Alberta in real-time.
Methods
For information on how the results in this indicator were calculated and for references, see Condition of the Environment Report – Air Component
Summary of key results
Last updated: February 2025
- Changes in PM2.5 monitoring equipment over the last 20 years mean that statistical testing for trends over time is not possible (for additional information see the ‘data limitations’ section).
- The highest concentrations of PM2.5 in Alberta are caused by wildfire smoke and can reach concentrations that exceed the Alberta Ambient Air Quality Objective, which is based on the protection of human health.
- The location and severity of smoke varies year-to-year depending primarily on wildfire activity and intensity. For more information on wildfire smoke impacts on air quality in Alberta, see: Wildfire Smoke Air indicator.
- Human activities also significantly contribute to PM2.5 concentrations, primarily during winter smog episodes.
Variation across Alberta
- Annual average and peak concentrations of PM2.5 vary across Alberta (Figures 1a and 1b, respectively) and are driven primarily by wildfire smoke and winter smog.
- PM2.5 concentrations are highest in large population centres and near industrial emissions sources. Stations located outside of these areas (for example in regional locations and smaller communities) have lower PM2.5 concentrations.
- PM2.5 concentrations are also highest in areas affected by wildfire smoke.
- Wildfire smoke affects different parts of the province each year. The location of wildfires and the wind patterns that transport smoke determine which regions are affected. For more information on how wildfire smoke affects air quality in Alberta, see: Wildfire Smoke – Air indicators.
- In 2023, wildfire smoke impacted much of the province throughout the spring and summer. Wildfires burning in northern B.C. and Alberta impacted air quality in May and June, while wildfires burning in northern Alberta, B.C. and the southern Northwest Territories affected air quality from July to September.
Figure 1a. Annual average PM2.5 concentrations across Alberta for 2023
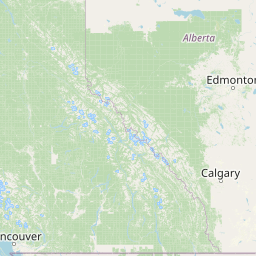
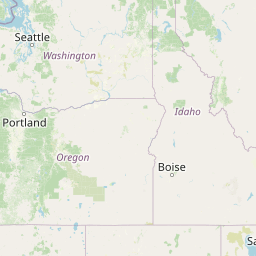
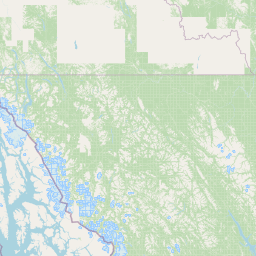
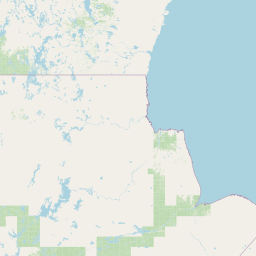

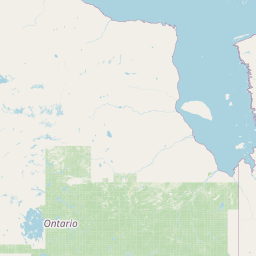
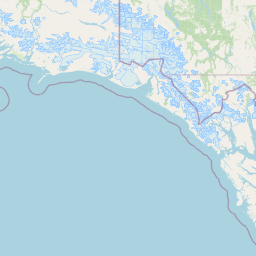

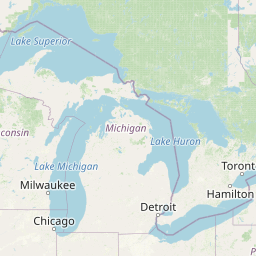
PM2.5 Annual Average (µg m-3)
22.2 - 27.117.4 - 22.1
12.6 - 17.3
7.8 - 12.5
Select a circle on the map to view the 2023 concentration for a specific monitoring station.
Source: Government of Alberta
Figure 1b. Peak PM2.5 concentrations across Alberta for 2023


















PM2.5 Peak (µg m-3)
161.1 - 199.5122.7 - 161
84.3 - 122.6
45.9 - 84.2
Select a circle on the map to view the 2023 concentration for a specific monitoring station. Peak concentrations are calculated as the annual 98th percentile of daily average concentrations.
Source: Government of Alberta
Changes over time
- The difference in PM2.5 concentrations between years is largely driven by the extent of wildfire smoke and the frequency and severity of winter smog episodes (Figures 2a and 2b).
- The highest annual average PM2.5 concentrations between 2000 and 2023 occurred in 2023 due to an extreme wildfire season in western Canada (see the Wildfire Smoke Air Indicator). However, the highest peak PM2.5 concentrations between 2000 and 2023 occurred in 2016 due to the Horse River wildfire near Fort McMurray.
- Annual average and peak PM2.5 concentrations were low in 2020, when there was reduced wildfire activity in Alberta and limited impact from wildfires in surrounding jurisdictions. Actions taken in response to COVID-19 may have also affected PM2.5 due to reductions in emissions of air pollutants from sources such as vehicle traffic.
- Trends over time for PM2.5 cannot be tested statistically because of changes in monitoring equipment (see limitations section below).
Figure 2a. Trends in annual average PM2.5 concentration from 2000 to 2023 at large population centres
Chart data table
| Year | Provincial Average | 10th Percentile | 90th Percentile | Calgary | Edmonton | Fort McMurray | Grande Prairie | Lethbridge | Medicine Hat | Red Deer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 8.1 | 6.3 | 10.8 | 10.1 | 11.3 | 6.5 | ||||
| 2001 | 7.2 | 3.3 | 9.7 | 9.5 | 10.2 | 6.9 | 8.6 | |||
| 2002 | 5 | 2.9 | 6.9 | 6.3 | 6.9 | 4.7 | 5.5 | |||
| 2003 | 5.6 | 3.2 | 7.7 | 8.1 | 7.3 | 3.6 | 5.7 | |||
| 2004 | 4.9 | 3.2 | 6.7 | 6.4 | 6.5 | 4.2 | 4.1 | 3.1 | 5 | |
| 2005 | 4.5 | 3.3 | 6.5 | 5.5 | 5.4 | 3.6 | 4.6 | 3.3 | 3.1 | 4.5 |
| 2006 | 5 | 3.8 | 6.9 | 6.6 | 5.7 | 4.3 | 5.2 | 4 | 3.5 | 5.4 |
| 2007 | 4.8 | 3.4 | 7 | 5.7 | 5.3 | 4.6 | 4 | 3.6 | 3.5 | 4.2 |
| 2008 | 4.9 | 3.4 | 6.9 | 5.7 | 6 | 4.9 | 4.1 | 3.6 | 3.4 | 4.4 |
| 2009 | 5.5 | 3.7 | 8.5 | 9 | 7.9 | 4 | 4.8 | 3.8 | 8.6 | |
| 2010 | 8.2 | 4.6 | 14.4 | 11.4 | 14.8 | 4.6 | 10.8 | 7.7 | 16.2 | |
| 2011 | 6.9 | 3.4 | 10.3 | 10.9 | 9.7 | 8.2 | 8.4 | 6.6 | 7.8 | 13.7 |
| 2012 | 6.9 | 4.6 | 9.4 | 10 | 8.7 | 6 | 6.5 | 9.4 | 10.2 | |
| 2013 | 6.4 | 3.6 | 8.6 | 8.1 | 8.7 | 6.4 | 6.3 | 7 | 10.4 | |
| 2014 | 7 | 4.3 | 9.1 | 8.2 | 9.8 | 8 | 8.2 | 7.1 | 4.8 | 7.1 |
| 2015 | 7.1 | 4.1 | 9.4 | 8.1 | 9 | 8.5 | 6.4 | 8.2 | 6.6 | 8.8 |
| 2016 | 6.6 | 3.9 | 9.7 | 5.2 | 7.3 | 19 | 6.1 | 4.8 | 4 | 5.7 |
| 2017 | 6.4 | 4.5 | 8 | 7.9 | 7.9 | 5.9 | 6.7 | 7.5 | 5.8 | 6.8 |
| 2018 | 8.8 | 6.6 | 11.6 | 11.2 | 10.2 | 7.6 | 9.9 | 9.3 | 6.9 | 9.5 |
| 2019 | 6.2 | 4.6 | 7.7 | 7.1 | 7.6 | 6.2 | 6.9 | 5.4 | 4.6 | 6.9 |
| 2020 | 4.9 | 3.4 | 6.6 | 6.3 | 6 | 4.8 | 4.9 | 5.3 | 5.2 | 5.2 |
| 2021 | 6.9 | 4.9 | 8.5 | 8.4 | 8.5 | 6 | 6.1 | 7 | 7.2 | 7.4 |
| 2022 | 6.3 | 4.9 | 7.9 | 7.1 | 7.9 | 6.6 | 6.2 | 6.1 | 5.1 | 6.3 |
| 2023 | 16.1 | 10.7 | 23.3 | 12.4 | 19.1 | 21.1 | 23.3 | 7.8 | 7.8 | 13.5 |
Source: Government of Alberta
Chart description
Line chart showing the change over time in annual average PM2.5 concentrations for large urban centres in Alberta, the provincial average, and the 10th and 90th percentile of all PM2.5 monitoring stations in the province. Years that are impacted more by wildfire smoke and wintertime smog episodes have higher annual average concentrations (for example: 2010, 2016 at Fort McMurray, and 2023).
Figure 2b. Trends in peak PM2.5 concentrations from 2000 to 2023 at large population centres
Chart data table
| Year | Provincial Average | 10th Percentile | 90th Percentile | Calgary | Edmonton | Fort McMurray | Grande Prairie | Lethbridge | Medicine Hat | Red Deer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 17.6 | 13.5 | 23.7 | 22 | 24.9 | 13.7 | ||||
| 2001 | 17.5 | 9.5 | 22.4 | 20.8 | 24 | 15.9 | 20.9 | |||
| 2002 | 17.7 | 11.5 | 24.5 | 18.8 | 23.4 | 15.2 | 15.3 | |||
| 2003 | 19.9 | 11.5 | 33.5 | 35.3 | 24 | 11.5 | 20.9 | |||
| 2004 | 17.6 | 13.6 | 21.6 | 17.6 | 21.4 | 17.5 | 14.2 | 15.7 | 13.8 | |
| 2005 | 12.9 | 8.9 | 16.6 | 13.2 | 14.4 | 12.7 | 14.8 | 10.1 | 8.8 | 10 |
| 2006 | 14.9 | 11.7 | 18.4 | 18.3 | 17.8 | 14.1 | 16.4 | 12.3 | 9.5 | 14.5 |
| 2007 | 14 | 10.3 | 16.8 | 16.2 | 14.8 | 15.1 | 11.9 | 12 | 10.5 | 11.8 |
| 2008 | 14.3 | 9.8 | 19.9 | 14.5 | 18.6 | 14.9 | 11.5 | 9.8 | 10 | 11.6 |
| 2009 | 16.1 | 11.9 | 22.4 | 19.5 | 21.5 | 13.9 | 14.7 | 12.5 | 24.3 | |
| 2010 | 28 | 16.3 | 41.4 | 30.8 | 46.4 | 16.4 | 29.1 | 25.7 | 37.5 | |
| 2011 | 26.9 | 11.3 | 60.5 | 24 | 26.9 | 72.4 | 20.3 | 18.5 | 18 | 34.1 |
| 2012 | 21.3 | 13.3 | 31.5 | 21.9 | 22.3 | 20.8 | 19.5 | 23.4 | 22.3 | |
| 2013 | 18.1 | 10.3 | 24 | 20.8 | 29.5 | 17 | 17.6 | 17.1 | 34.5 | |
| 2014 | 25.7 | 16.7 | 34.1 | 21.2 | 26 | 35.1 | 35.9 | 20.9 | 16.5 | 20.4 |
| 2015 | 31.9 | 17 | 48.1 | 28.1 | 23.7 | 40.9 | 20.9 | 42 | 45.5 | 24.5 |
| 2016 | 31.3 | 11.9 | 49.4 | 14.7 | 22.7 | 208.4 | 21 | 14.6 | 10.7 | 16.5 |
| 2017 | 25.8 | 14.9 | 34.9 | 34.6 | 29 | 15.9 | 26.3 | 44.9 | 29.3 | 29 |
| 2018 | 51.9 | 32.8 | 65.9 | 58.1 | 49.1 | 35.4 | 60.5 | 58.4 | 43 | 50.5 |
| 2019 | 21.5 | 15.3 | 28 | 19.2 | 26.2 | 21.2 | 23.8 | 20.8 | 13.7 | 18 |
| 2020 | 15.3 | 9.4 | 19.8 | 18.9 | 20.1 | 11.5 | 17.9 | 20.5 | 16.3 | 15.6 |
| 2021 | 32.3 | 25 | 41 | 44.2 | 37.8 | 24.6 | 29.7 | 39.5 | 38.2 | 32.8 |
| 2022 | 24.1 | 18.5 | 32.3 | 24.9 | 28.4 | 24.1 | 25.5 | 22.5 | 14.8 | 19 |
| 2023 | 104 | 61 | 162.2 | 62.2 | 111.9 | 145.3 | 162.2 | 46.8 | 47 | 89.8 |
Source: Government of Alberta
Chart description
Line chart showing the change over time in peak PM2.5 concentrations for large urban centres in Alberta, the provincial average, and the 10th and 90th percentile of all PM2.5 monitoring stations in the province. The highest peak concentration was measured in Fort McMurray in 2016 with a value of 208.4 μg/m3. Years that are impacted more by wildfire smoke and wintertime smog episodes have higher peak concentrations (for example: 2016 at Fort McMurray specifically and 2023 province-wide).
Seasonal variation
- Higher concentrations of PM2.5 occur during periods affected by wildfire smoke (Figure 3).
- Elevated concentrations also occur from November to March during winter smog episodes caused by human activities. Winter smog has a smaller effect on PM2.5 concentrations compared to wildfire smoke, which is why smog contributions are not as apparent in Figure 3 as those from wildfires.
- Winter smog typically occurs during temperature inversions, when cold air is trapped along with pollutants at ground level preventing mixing and dispersion of pollutants.
- PM2.5 concentrations can also be elevated at other times of year due to summer smog episodes, high wind dust events and other local causes (for example, construction).
Figure 3. Seasonal variation in monthly average PM2.5 for 2020 to 2023, shown using bar plots of the median monthly value across all long-term air monitoring stations. Whiskers extend from the top of the bar to the maximum monthly value across all stations. Major wildfire episodes are indicated for each year.

- Alberta's Ambient Air Quality Objectives provide thresholds for over 30 airborne compounds to protect human and ecosystem health. The AAAQOs are used in the design of industrial facilities and to establish emissions requirements. The Alberta Government tracks AAAQO exceedances and assesses the need for management action.
- Exceedances of the 24-hour AAAQO for PM2.5 are mainly caused by wildfire smoke and winter smog episodes (Figure 4). In 2023, there were 2,275 exceedances of the 24-hour AAAQO for PM2.5 in various locations across Alberta, almost 9 times greater than in 2022. The most frequent exceedances were observed at the Fort Hills station (93) in northeastern Alberta, followed by the Fort McKay South station (82), also in northeastern Alberta. The AAAQO for PM2.5 is 29 µg/m3 for 24-hour periods based on the protection of human health.
Figure 4. Cause of PM2.5 exceedances in 2023 across Alberta
Chart data table
| Category | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Wildfire | 95 |
| Winter smog and controlled burns | 4.7 |
| Other | 0.3 |
Source: Government of Alberta
Chart description
Pie chart showing causes of PM2.5 exceedances in 2023 across Alberta.
Air quality reporting and resources
- Alberta reports annually on the status of air quality for existing regional air quality management frameworks (AQMFs) as well as the Canadian Ambient Air Quality Standards (CAAQS).
- PM2.5 is one of the pollutants reported on through the South Saskatchewan Region (SSR) AQMF as well as the CAAQS.
- The most recent assessment results are available in Alberta’s Air Zone Reports.
- Published reports and scientific papers on air quality in Alberta are available via the Air Indicators landing page under ‘Related Publications’.
- Alberta also provides air quality data and information to the public through the near real-time AQHI website and provides access to quality assured data via Alberta’s Air Data Warehouse.
Data limitations
- Between 2010 and 2017, older equipment at Alberta’s air monitoring stations was replaced with new monitoring equipment for PM2.5. These new monitors measure an additional portion (semi-volatile) of the PM2.5 mass not captured by older monitors.
- As older monitoring equipment used between 2000 and 2017 likely underreported concentrations of PM2.5 under some conditions, after 2010, the increase in PM2.5 concentrations may be a result of changes in monitoring equipment. Most importantly, concentrations measured with the new monitors may not be directly comparable with measurements from years in which older monitors were used.
Focused study
In response to an exceedance of the national Canadian Ambient Air Quality Standards (CAAQS) in the Red Deer area in the 2011-2013 assessment, a focused study was initiated to measure PM2.5 composition and precursor gases at 3 monitoring stations between 2017 and 2019. The objective of the study was to assess regional and local sources of PM2.5 and inform management actions to improve air quality.
Key findings include:
- Elevated PM2.5 concentrations were regional scale events, with similar and correlated concentrations observed at two stations in Red Deer, and at a site located 9.4 km upwind of the city.
- When wildfire-impacted samples were removed, PM2.5 concentrations were largest in the spring, and are dominated by the sulphate and nitrate factors (74%) (Figure 5).
- The sulphate factor was consistent with a regional source, which could have included the coal-fired power plants and the smaller upstream oil and gas operations in the area. The elevated nitrate factors appeared to be affected by local emissions sources, which could have included both urban and industrial sources, and been promoted by meteorological conditions.
- Reducing oxides of nitrogen could help to manage PM2.5 concentrations in the region.
Figure 5. Relative contribution to PM2.5 mass at Red Deer study monitoring sites during the 2017 to 2019 study period
Chart data table
| Category | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Road 2% | 2.43 |
| Biogenic <1% | 0.72 |
| Selenium 2% | 2.37 |
| Carryover 6% | 6.23 |
| Nitrate 56% | 56.13 |
| Fresh smoke <1% | 0.02 |
| Sulphate 18% | 18.42 |
| Secondary Organics 11% | 11.40 |
| Crustal matter 2% | 2.28 |
Table description
Pie chart showing relative contribution to PM2.5 mass at the Red Deer study monitoring sites. The nitrate and sulphate factors have the largest contribution, at 56% and 18%, respectively. Secondary organics are the third largest contributor at 11%. The remaining 15% is made up of six factors (carryover, road, selenium, crustal matter, biogenic, and fresh smoke).